Bioavailability and solubility enhancement services
Approximately 70-90% of drugs in development have solubility and bioavailability challenges, requiring special attention on enabling technologies and formulations.
The majority of pipeline drugs experience poor solubility
Solubility of oral solid dose drugs presents an increasing threat to drug development pipelines as a growing majority of current candidate molecules are poorly soluble. If a drug cannot be dissolved to enter the bloodstream through the gastrointestinal tract, it will not reach systemic circulation and won’t be available to provide its intended effect. Thus, to solve bioavailability challenges, solubility must first be addressed.
Many solubility enhancement technologies and formulation options are available to developers, and the choices can be overwhelming. That’s why working with a partner with extensive experience and deep expertise in both API and formulation development and manufacturing is so critical.
Quadrant 2TM
Predictive computational modeling using Patheon’s Quadrant 2™ platform can help you avoid months and even years of formulation setbacks. You provide your API’s chemical structure, any known physiochemical properties, and business and clinical objectives, and the Quadrant 2 platform will predict the solubility enhancement technology and excipient combinations that are most likely to succeed.
90%
Technology selection accuracy
80%
Formulation selection accuracy
Bioavailability enhancement techniques
Micronization via jet pulverizing is a method used to enhance the surface area of drug particles available for dissolution by creating a granular material from a powder or solid substance. The jet-milling process utilizes either a fluidized bed or a centrifugation air jet pulverizer (pictured).
Micronization takes place in a shallow, cylindrical chamber where a high-pressure air stream is injected along with the drug feed, creating a vortex where size reduction is a result of the high-velocity collisions between particles. Large particles are held in the chamber via centrifugal force, and micronized particles migrate toward the central discharge port as they progressively reduce in size.
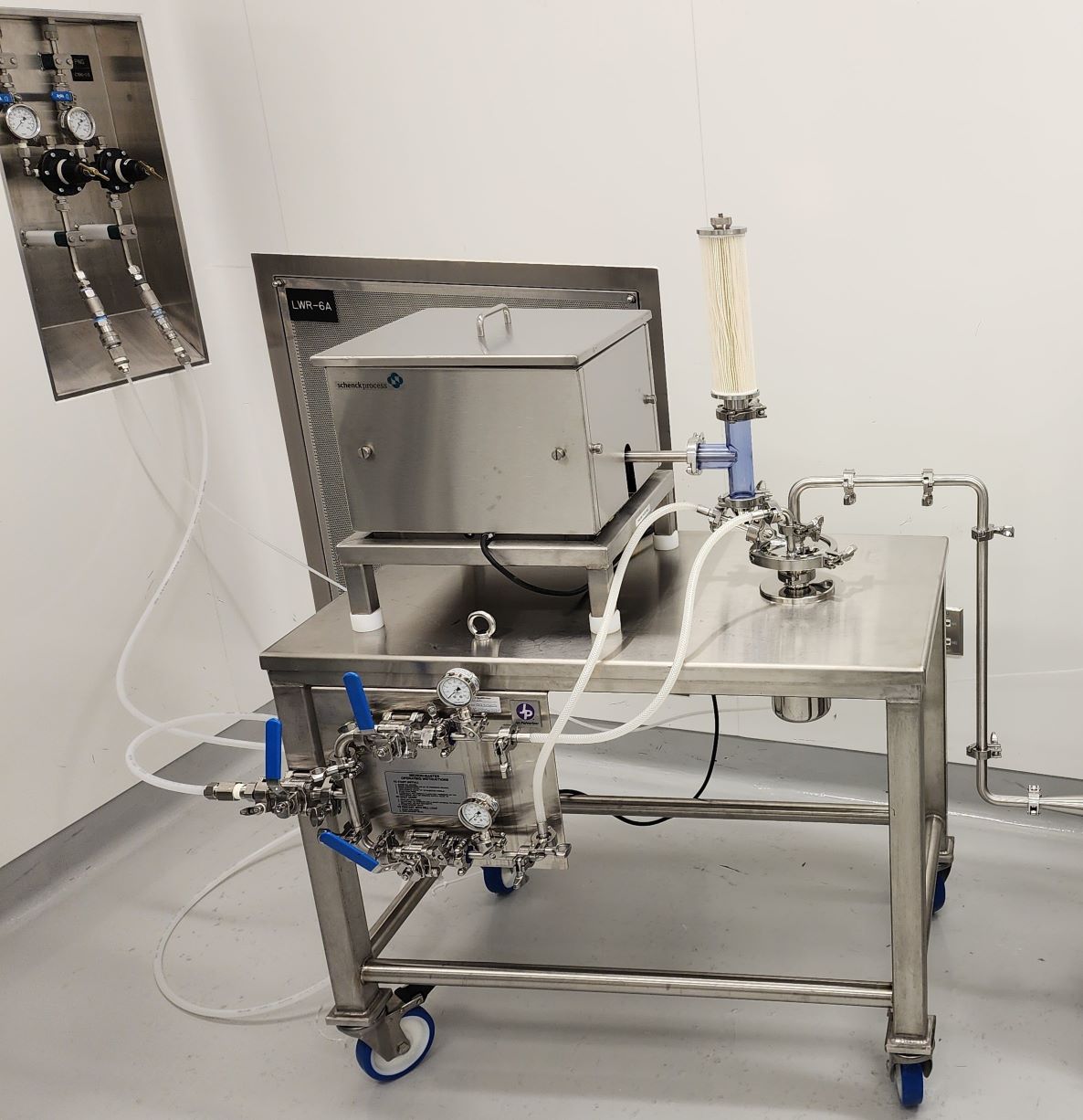

Spray drying is one method of stabilizing a drug via amorphous solid dispersion (ASD) that creates an appropriately sized microparticle of drug-polymer through a controlled process.
Hot melt extrusion (HME) is a solvent-free enhancement technology that processes material using temperature and shear. Finding an appropriate stabilizing polymer is a critical first step in the HME process. Analytical tools are used to understand the thermal properties of APIs and polymers, and in conjunction, Patheon’s Quadrant 2™ predicts optimal drug-polymer combinations and ratio options by assessing compatibility between functional groups (1). Once identified, the API and polymer are fed into the extruder (2) where the individual components are melted, mixed, homogenized, shaped by pressing through a die opening, (3), and then cooled and pelletized (4).
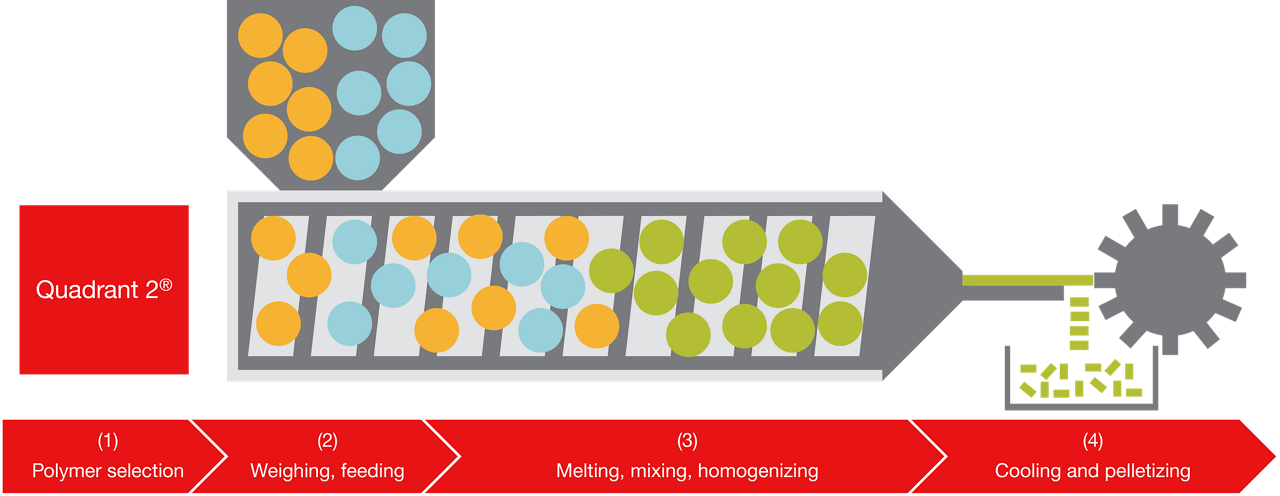
Thermo Fisher Scientific can create micro-pellets that range from micrometers to a few millimeters; cut rods that range from millimeters to a few centimeters; and granules that can all be further processed or coated to prepare the final formulations, including delayed- or sustained-release tablets.
Lipid formulations are commonly used in pharmaceutical and biotechnological industries to bolster pharmacological efficacy by improving the solubility of poorly water-soluble drugs.
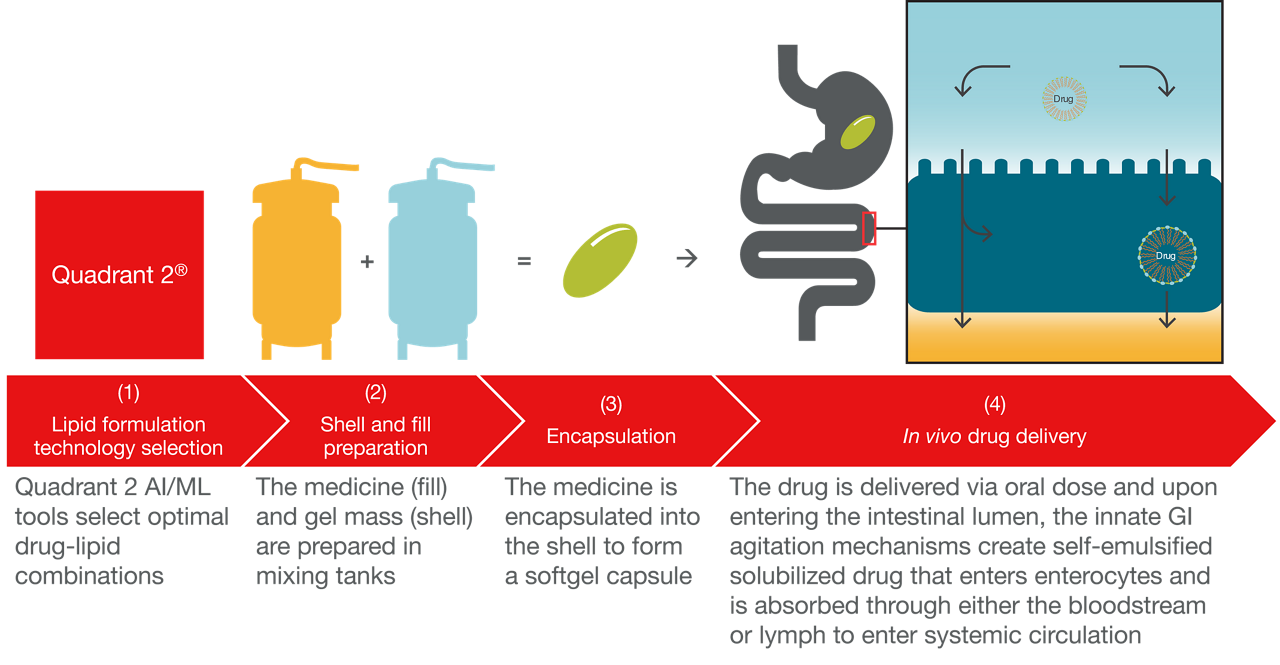
Lipid-based technologies are designed to enhance a drug’s dissolution kinetics in the gastrointestinal tract (GIT) by maintaining a solubilized state during in vivo dispersion, digestion, and absorption of the drug that can contribute to overall improved bioavailability. Softgel is the most versatile OSD for in vivo delivery of these lipid-based formulations. Manufacturing softgels using a rotary die process follows three steps:
(1) Gel mass (shell) preparation
(2) Medicine (fill) preparation
(3) Encapsulation of the medicine fill in the shell to form a hermetically sealed softgel capsule
The elegance of using lipid technology for poorly soluble drugs is the ability to deliver the drug in a liquid or semi-solid formulation, where the innate agitation mechanisms in the GIT create stable drug emulsions in solubilized or supersaturated states that can be absorbed into the bloodstream, improving bioavailability and drug efficacy (4).
Advantages of using lipid formulations:
- Improved bioavailability
- Enhance drug absorption
- Stabilization of drug molecule
- Flexible formulation options
- Reduced food effect
- Patient compliance
Finding the most appropriate physical form for your API is critical, as this impacts the downstream performance of your product. Optimizing characteristics such as size and shape, particle size distribution, flow, density, bioavailability, and melting point enables more efficient formulation and manufacturing process development at the drug product stage. Our extensive capabilities and experience in solid-state chemistry ensure that you receive the best solid form for your drug product development and scale-up.
Advantages of solid state chemistry:
- Better understanding of API chemical properties to ensure API stability, developability, and formulation fit
- Improved solubility of poorly water-soluble API
- Improved or optimized crystal modification, size and distribution, yield, purity, and processability
| Basic characterization |
Amount: 1-2 grams Time: 2 weeks |
Recommended for all APIs at preclinical through Phase 1. |
Data typically gathered during characterization:
|
| Polymorph screening |
Amount: 5-10 grams Time: 8-12 weeks |
Polymorphs can have significantly different chemical, physical, and potentially, pharmaceutical activity. The selected form can also have a direct impact on the ability to reproducibly manufacture both the API and the drug product. |
Polymorph screens typically consist of:
|
| Salt screening | Amount: 5-10 grams Time: 8-12 weeks |
Developing a salt for a new molecule can support improvements in molecule solubility, processability, and bioavailability. |
|
| Early crystallization process development | Time: 4 weeks |
Developing a crystalline drug substance has a positive impact on the molecule’s long-term stability and processability. |
Crystal process development typically consists of:
|
Helpful resources
Helpful Resources

